Esr df and q are all aspects of the performance of a capacitor that will affect its performance in areas such as rf operation.
Ceramic capacitor power dissipation.
All sales are subject to the.
A ceramic capacitor is a fixed value capacitor where the ceramic material acts as the dielectric it is constructed of two or more alternating layers of ceramic and a metal layer acting as the electrodes the composition of the ceramic material defines the electrical behavior and therefore applications.
Simply stated df is a measure of power lost traveling through a capacitor.
Refer to this chart for capacitor value change by temperature per dielectric.
Of a capacitor being measured drops excessively which prevents correct measurement of capacitance and dissipation factor of the capacitor.
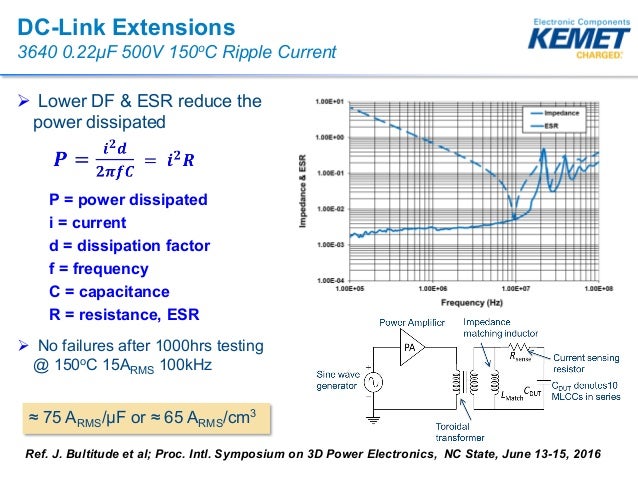
However esr and df are also particularly important for capacitors operating in power supplies where a high esr and dissipation factor df will result in large amount of power being dissipated in the capacitor.
Depending on type of lcr meter used measurement of a ceramic capacitor with large capacitance such as 10µf at an assigned voltage may be impossible due to extremely low impedance of such capacitor.
Introduction capacitors are frequently used in circuits that expose them to significant ripple voltage and current.
Recall that depending on the dielectric used the value of a capacitor also changes over temperature.
This loss is mainly in the form of heat which compounds the loss as the resulting temperature rise can cause additional problems such.
Dissipation factor vs ac volts x7r capacitance vs ac volts x7r type ac power ac high voltage ac power ceramic capacitors johanson dielectrics inc.
If the capacitor is used in an ac circuit the dissipation factor due to the non ideal capacitor is expressed as the ratio of the resistive power loss in the esr to the reactive power oscillating in the capacitor or when representing the electrical circuit parameters as vectors in a complex plane known as phasors a capacitor s dissipation factor is equal to the tangent of the.
Power is dissipated in the resistive component of the capacitor s impedance by the ripple current and this power dissipates heat which causes the capacitor s temperature to rise.
This is a general set of guidelines and recommendations for reducing capacitor power dissipation with increasing ambient temperature.
Dissipation factor of ceramic capacitors.
Either the maximum voltage rating or the maximum power dissipation of the part limits the maximum current through a capacitor.