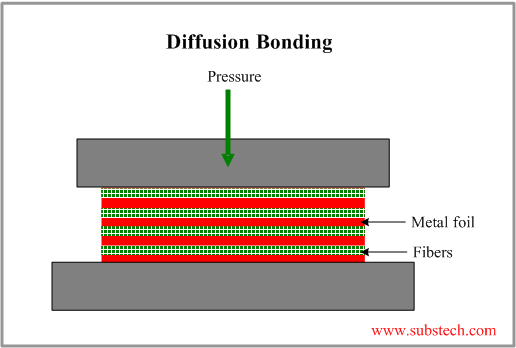
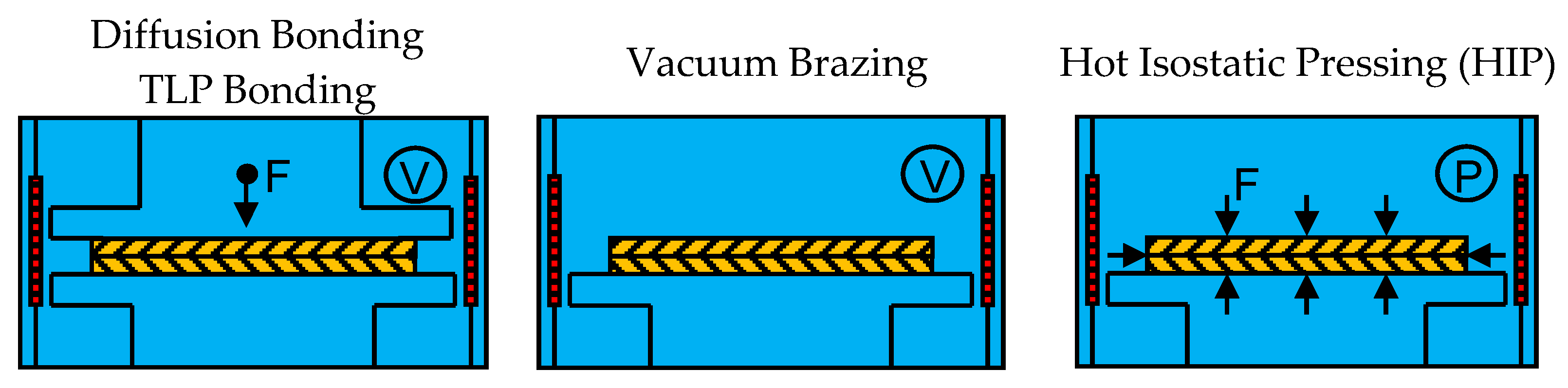
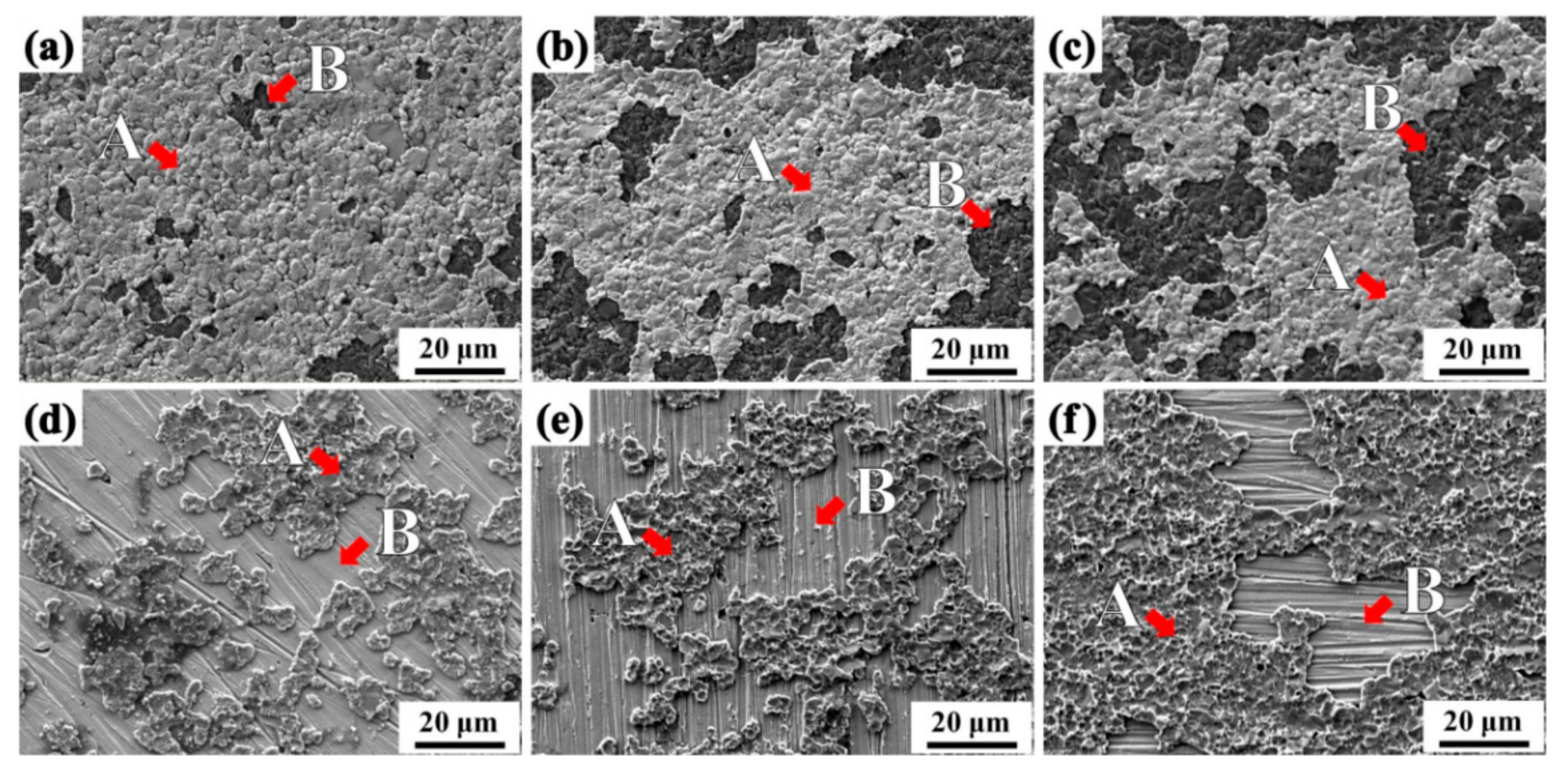
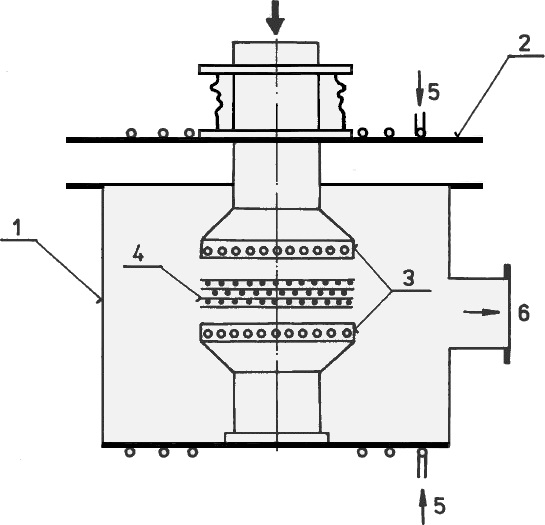
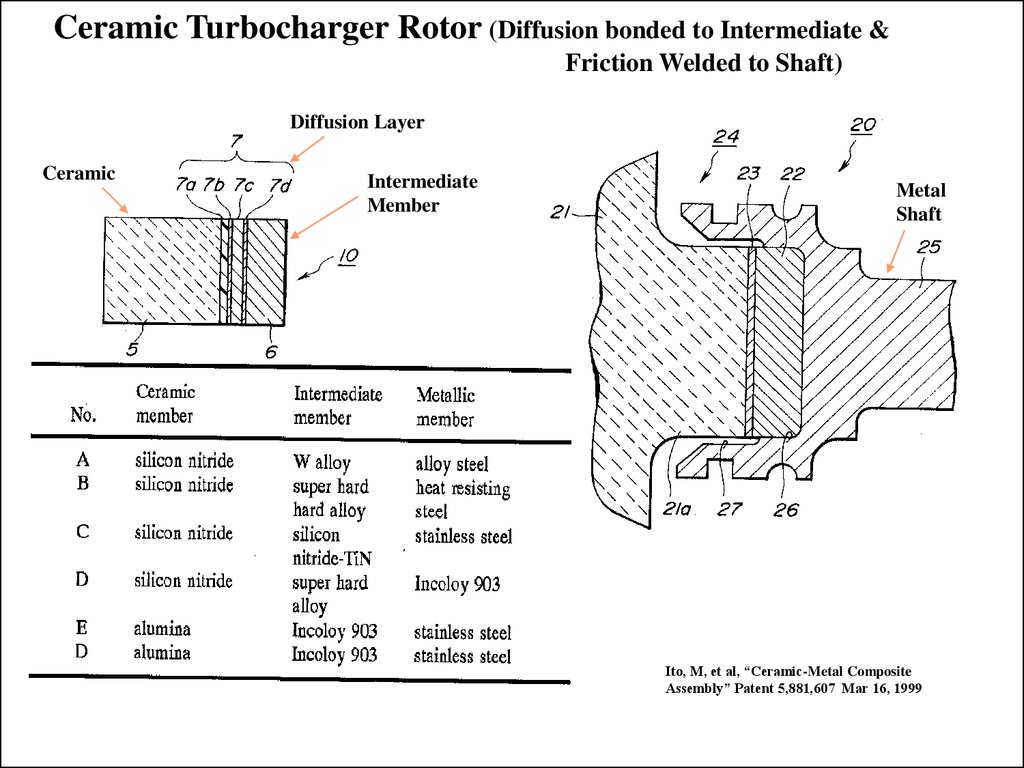
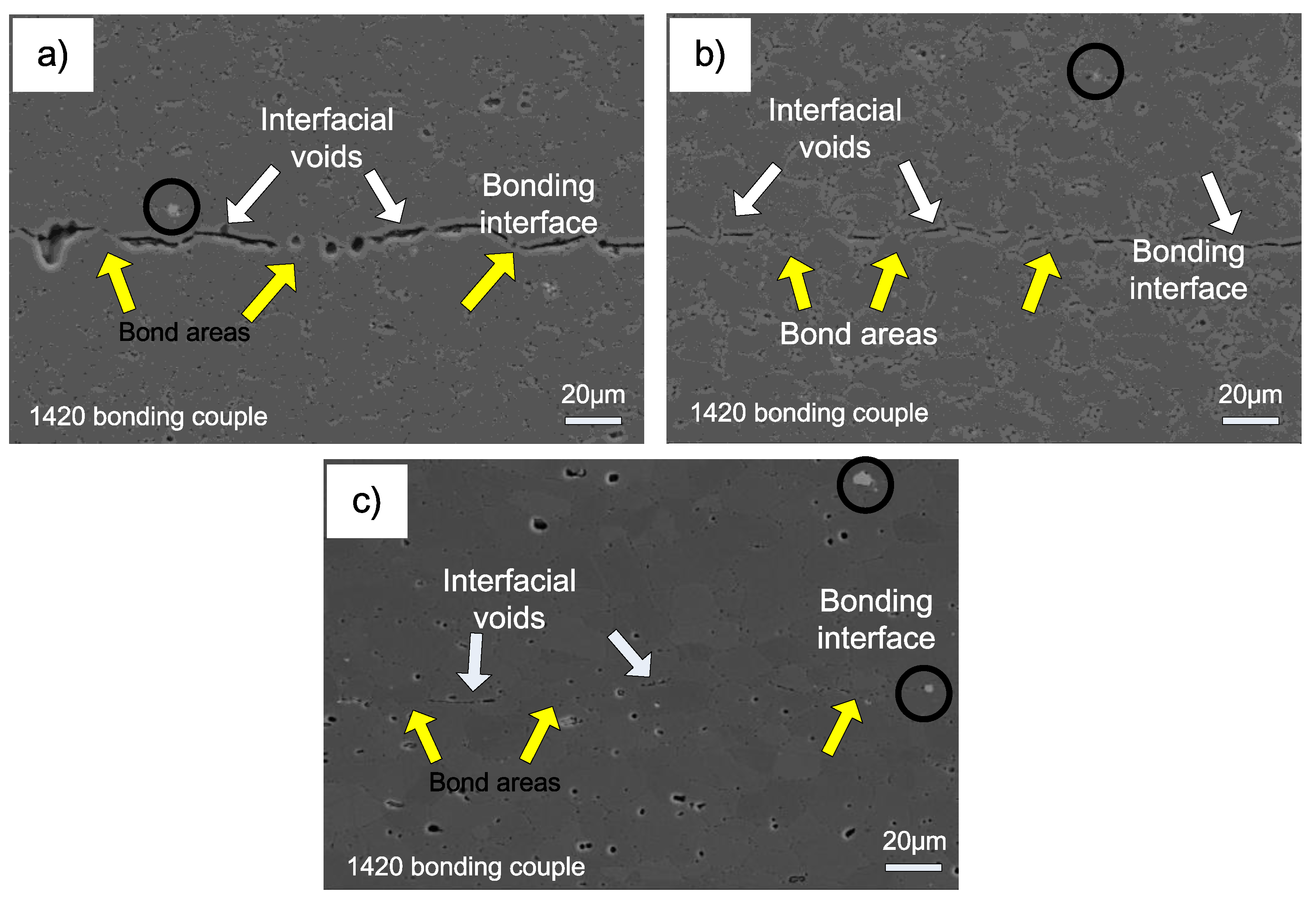
Diffusion bonding of ceramic materials is usually a direct joining method that accomplishes joining between two often like materials through atomic level mass transport and exchange.
Ceramic diffusion bonding.
These include principal bonding parameters such as temperature time and pressure.
Diffusion bonding of ceramics to ceramics and to metals is reviewed with primary emphasis on the effects of operational variables on joint strength.
The process is dependent on a number of parameters in particular time applied pressure bonding temperature and method of heat application.
Diffusion bonding is a solid state joining process capable of joining a wide range of metal and ceramic combinations to produce both small and large components.
Diffusion bonding or diffusion welding is a solid state welding technique used in metalworking capable of joining similar and dissimilar metals.
However the process can be facilitated by interposing a metallic or glassy interlayer between the two substrates.
The mechanism is solid state diffusion or more properly inter diffusion.
This technique can similarly be used when joining ceramics to metals.
In addition the influence of atmosphere mismatch in coefficient of thermal expansion between the joint members interlayers and surface structure are discussed.