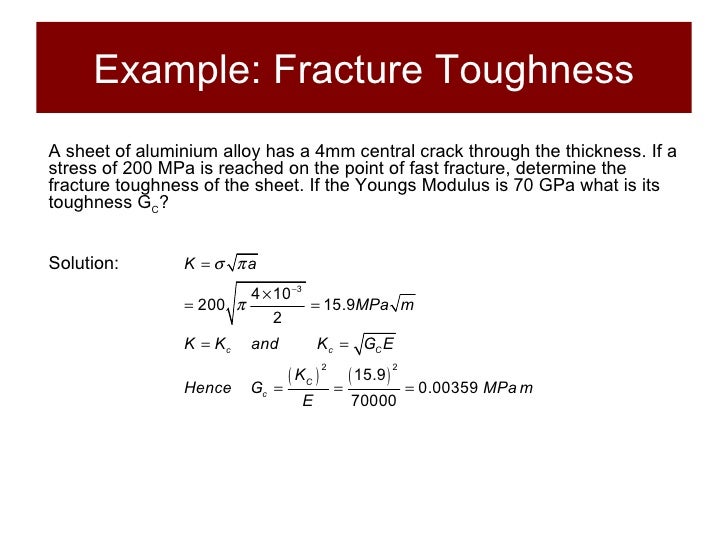
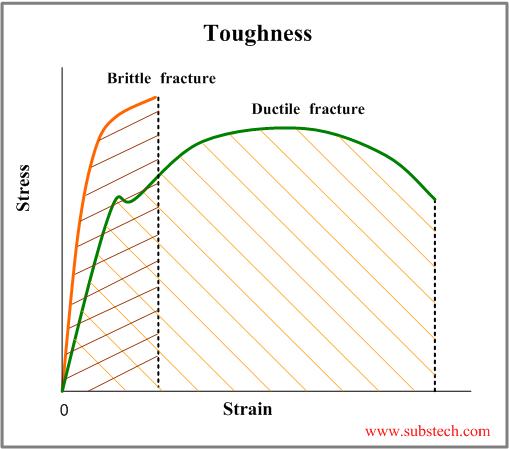
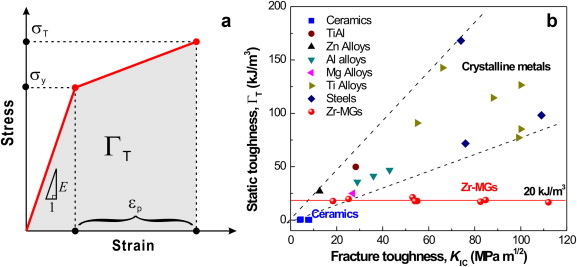
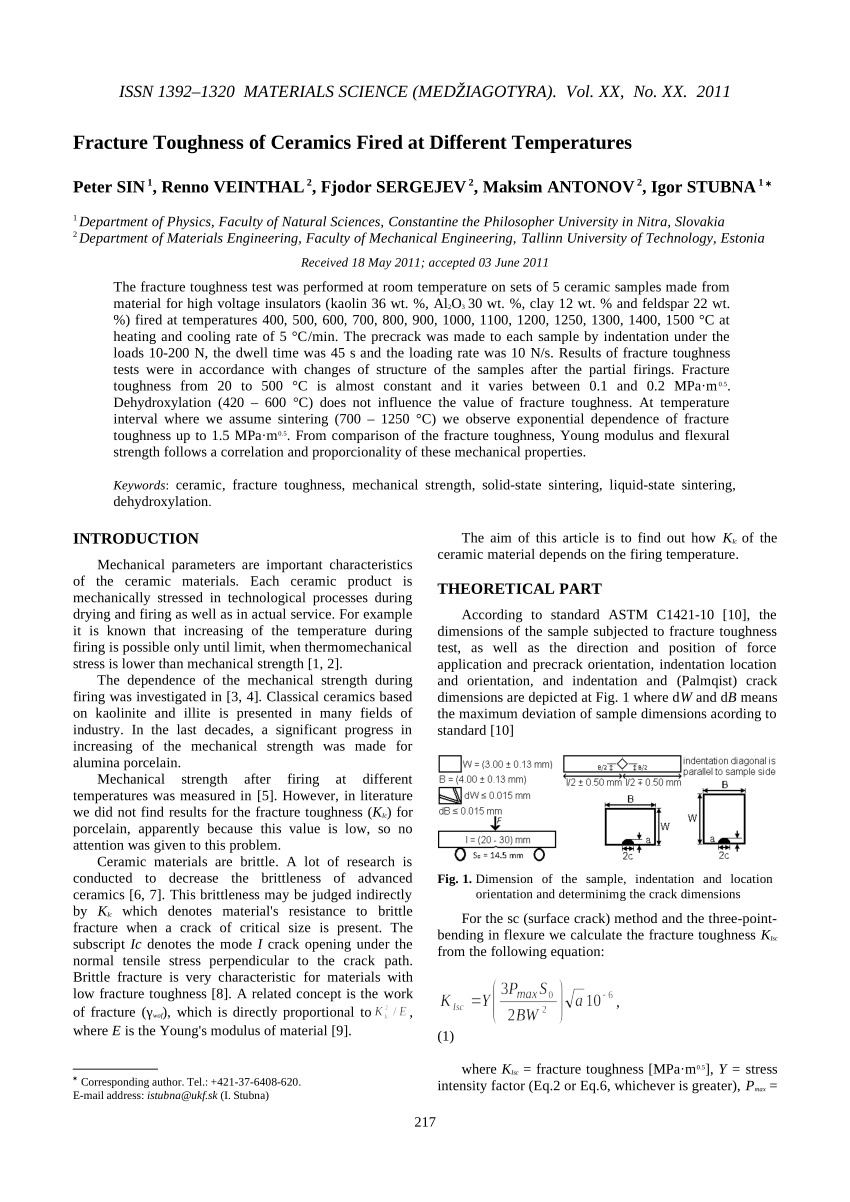
When a material of unknown fracture toughness is tested a specimen of full material section thickness is tested or the specimen is sized based on a prediction of the fracture toughness.
Ceramic fracture toughness equation.
Fracture toughness of ceramics by the vickers indentation crack length method.
The microstructure fracture toughness and associated toughening mechanisms of the composites were investigated.
In modern materials science fracture mechanics is an important tool used to improve the.
The fracture toughness of the sintered material was evaluated by jis r 1607 japanese industrial standard related to fine ceramics method using miyoshi s equation 4 16 125 126.
The fracture of the brittle ceramics is usually controlled by the mode i fracture toughness.
From this equation a stress intensity factor k can be defined.
Fracture mechanics is the field of mechanics concerned with the study of the propagation of cracks in materials.
K c is referred to as the fracture toughness of the material.
Al 2 o 3 zro 2 3y sic ceramic composites were prepared by spark plasma sintering.
Fracture toughness of ceramics by the vickers indentation crack length method.
The fracture toughness value 9 11.
If k c is known the following can be derived from the equation.
Quinn national institute of standards and technology 100 bureau drive gaithersburg md 20899 8529 abstract fracture toughness is an important property that characterizes a material s brittleness or resistance to fracture.
The fracture toughness of composites made by combining engineering ceramics with engineering polymers greatly exceeds the individual fracture toughness.
If the fracture toughness value resulting from the test does not satisfy the requirement of the above equation the test must be repeated using a thicker specimen.
Ceramic engineering and science proceeding 27 3 45 62.
A critical review george d.
On the vickers indentation fracture toughness test.
Ceramics have a lower fracture toughness but show an exceptional improvement in the stress fracture that is attributed to their 1 5 orders of magnitude strength increase relative to metals.
It uses methods of analytical solid mechanics to calculate the driving force on a crack and those of experimental solid mechanics to characterize the material s resistance to fracture.
We can therefore say that fast fracture occurs when a critical stress intensity factor k c is reached ie.
The fracture toughness k 1c of the material was evaluated by indentation technique using different types of empirical formulas between 29 4 n and 98 n the calculated k 1c values depend on the crack profile and the applied load.
By analyzing the relationship between the indentation radius and the crack.
The fracture toughness first increased and then decreased with increasing the ndpo 4 reaching a peak value approximately 1 6 mpa m 1 2 at a content of 20 mol ndpo 4 which was almost 25 higher than that of ndybzr 2 o 7 ceramic.
Simple dimensional analysis of a body containing the crack with the length of 2a subjected to the stress shows that the stress intensification at the crack tip is.